title: 算法笔记-二叉树/线段树/排序树
index_img: ‘https://cdn.nlark.com/yuque/0/2023/png/2630542/1673112982757-5ae72879-a909-4654-a75e-8c64152f29ca.png'
hide: false
password: ‘’
date: 2019-10-10 17:24:22
categories: [算法相关]
必备知识 遍历方式
在树的题目当中主要围绕着,前序、中序、后续、广度、深度遍历来进行解题,所以掌握其十分重要,直接上迭代版本,递归太简单就不上了
前序遍历-通过栈实现 (先压入右结点)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return new ArrayList <>();else {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode tmp = stack.pop();if (tmp.right != null )if (tmp.left != null )return list;
中序遍历-通过栈实现 (一路向左把沿途结点压入栈)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return new ArrayList <>();else {new Stack <>();new ArrayList <>();while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (root != null ) {if (!stack.isEmpty()) {return list;
后序遍历-通过栈实现 (前序先push-left再reverse)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTreversal (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return new ArrayList <>();else {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode tmp = stack.pop();if (tmp.left != null ) {if (tmp.right != null ) {return list;
广度优先-通过队列实现
借助队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public void BFS (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();if (!Objects.isNull(root)) queue.add(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null ) queue.add(node.left);if (node.right != null ) queue.add(node.right);
深度优先-通过栈实现
借助栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public List<Integer> DFS (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode tmp = stack.pop();if (tmp.left != null ) stack.push(tmp.left);if (tmp.right != null ) stack.push(tmp.right);return list;
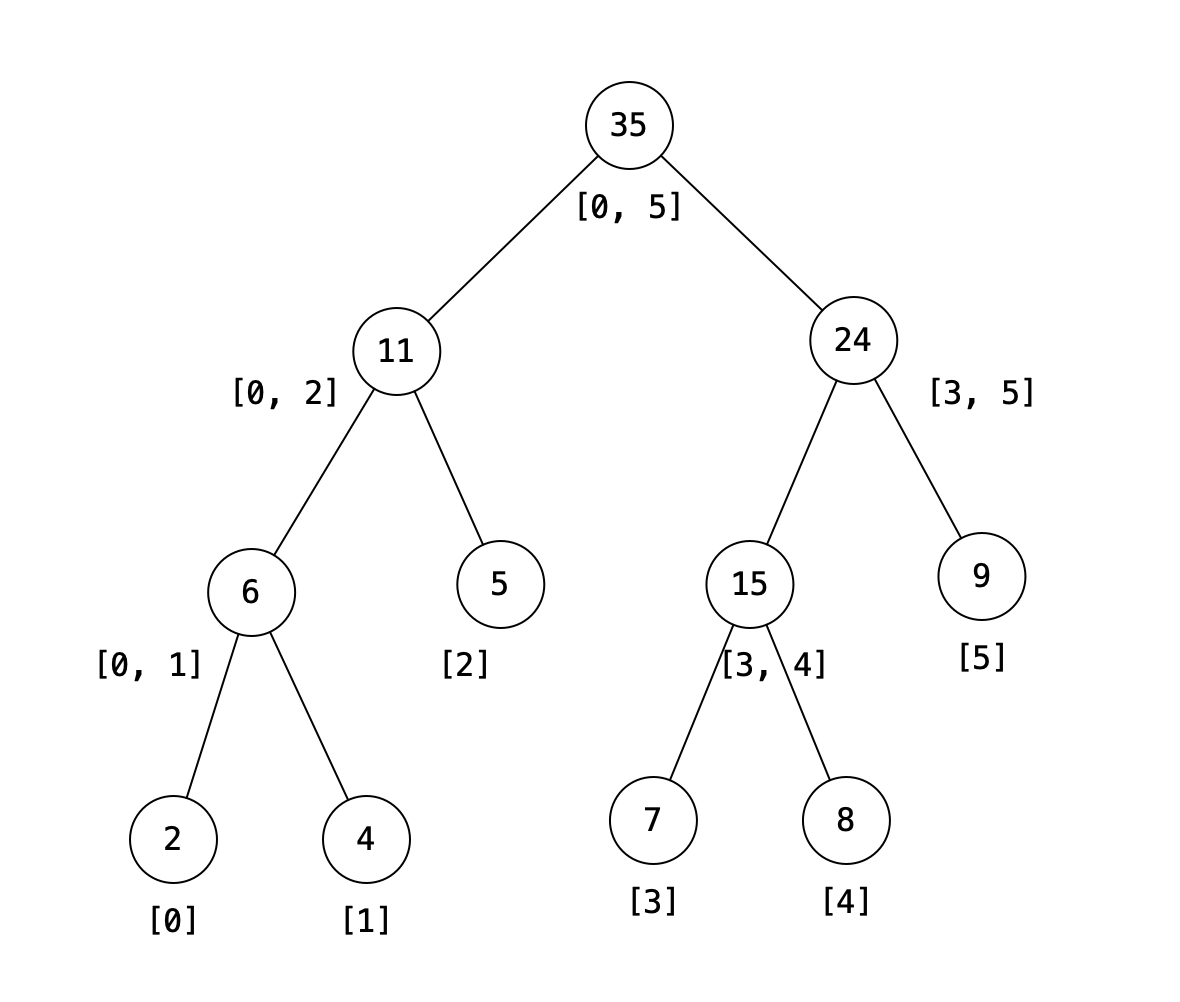
数类型 线段树 是一种非常灵活的数据结构,它可以用于解决多种范围查询问题,比如在对数时间内从数组中找到最小值、最大值、总和、最大公约数、最小公倍数等。
数组 A[0,1,…,n−1] 的线段树是一个二叉树,其中每个节点都包含数组的一个子范围 [i…j] 上的聚合信息(最小值、最大值、总和等),其左、右子节点分别包含范围
线段树既可以用数组也可以用树来实现。对于数组实现,如果索引 i 处的元素不是一个叶节点,那么其左子节点和右子节点分别存储在索引为 2i 和 2i+1 的元素处。
在上图所给出的示例中,每个叶节点都包含初始的数组元素 {2,4,5,7,8,9}。内部节点包含范围内相应元素的总和 - (11) 是从索引 0 到索引 2 的元素之和。而根节点 (35) 是它的两个子节点 (6) 和 (29) 的和,也是整个数组的和。
线段树可以分为以下三个步骤:
1.从给定数组构建线段树的预处理步骤。
2.修改元素时更新线段树。
3.使用线段树进行区域和检索。
相关题目 判断是否是平衡二叉树
判断树是否为平衡二叉树
测试用例
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
解题思路
平衡二叉树:左右子树高度差不超过一,根据这一特点,递归判断各个节点的子树是否符合条件,不满足则直接返回false,直到递归完成。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return true ;else return Math.abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);public int height (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;else return Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1 ;public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) {return depth(root)>=0 ;public int depth (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return 0 ;int left = depth(root.left);int right = depth(root.right);if (left==-1 ||right==-1 ||Math.abs(left-right)>1 )return -1 ;else return Math.max(left,right)+1 ;
特定深度节点链表
题目描述
给定一棵二叉树,设计一个算法,创建含有某一深度上所有节点的链表(比如,若一棵树的深度为 D,则会创建出 D 个链表)。返回一个包含所有深度的链表的数组。
示例
输入:[1,2,3,4,5,null,7,8]
1 2 3 4 5 1
/ 8
输出:[[1],[2,3],[4,5,7],[8]]
实现思路
通过广度优先遍历对树进行逐层遍历构造链表,通过每一次获取当前队列长度读取当前层的元素个数(关键)
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public static ListNode[] listOfDepth(TreeNode tree) {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();new ListNode (0 );for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {TreeNode treeNode = queue.poll();new ListNode (treeNode.val);if (treeNode.left != null ) queue.add(treeNode.left);if (treeNode.right != null ) queue.add(treeNode.right);return listNodes.toArray(new ListNode []{});
N叉树的前序遍历
题目描述
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的前序遍历。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
返回其前序遍历: [1,3,5,6,2,4]。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class Tree {new ArrayList <>();public List<Integer> preorder (Node root) {return list;public List<Integer> preorder (Node root) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();if (root == null ) {return list;while (!stack.empty()) {Node tmp = stack.pop();return list;
递归版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<Integer> preorder (Node root) {if (root==null )return new ArrayList <>();for (int i=0 ;i<root.children.size();i++){return ans;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public int maxDepth (Node root) {if (root==null )return 0 ;int max = 0 ;for (Node node:root.children){return max + 1 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (Node root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root==null )return ret;new LinkedList <>();while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();new ArrayList <>();for (int i=0 ;i<size;i++){Node node = queue.pop();if (node.children!=null &&node.children.size()>0 )queue.addAll(node.children);return ret;
最大二叉树
给定一个不含重复元素的整数数组。一个以此数组构建的最大二叉树定义如下:
二叉树的根是数组中的最大元素。 左子树是通过数组中最大值左边部分构造出的最大二叉树。 右子树是通过数组中最大值右边部分构造出的最大二叉树。 通过给定的数组构建最大二叉树,并且输出这个树的根节点。
示例 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 输入:[3,2,1,6,0,5]
提示:给定的数组的大小在 [1, 1000] 之间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;return build(nums,0 ,n-1 );public TreeNode build (int [] nums,int start,int end) {if (start>end)return null ;int maxIndex = start;for (int i=start+1 ;i<=end;i++)if (nums[i]>nums[maxIndex])maxIndex=i;TreeNode ret = new TreeNode (nums[maxIndex]);1 );1 ,end);return ret;
最大树定义:一个树,其中每个节点的值都大于其子树中的任何其他值。
给出最大树的根节点 root。
就像之前的问题那样,给定的树是从表 A(root = Construct(A))递归地使用下述 Construct(A) 例程构造的:
如果 A 为空,返回 null 否则,令 A[i] 作为 A 的最大元素。创建一个值为 A[i] 的根节点 root root 的左子树将被构建为 Construct([A[0], A[1], …, A[i-1]])
假设 B 是 A 的副本,并附加值 val。保证 B 中的值是不同的。
返回 Construct(B)。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,1,3,null,null,2], val = 5 输出:[5,4,null,1,3,null,null,2]
输入:root = [5,2,4,null,1], val = 3 输出:[5,2,4,null,1,null,3]
输入:root = [5,2,3,null,1], val = 4 输出:[5,2,4,null,1,3]
提示:
1 <= B.length <= 100
给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中第k大的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 示例 1:
限制: 1 ≤ k ≤ 二叉搜索树元素个数
解题思路
二叉搜索树、通过中许遍历得到递增序列、那么优先改变一下,从右子树先遍历即可得到递减序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {private int ans = 0 , count = 0 ;public int kthLargest (TreeNode root, int k) {return ans;private void helper (TreeNode root, int k) {if (root.right != null ) helper(root.right, k);if (++count == k) {return ;if (root.left != null ) helper(root.left, k);public int kthLargest (TreeNode root, int k) {new ArrayList <>();new Stack <>();if (root==null )return 0 ;while (root!=null ||!stack.isEmpty()){while (root!=null ){if (!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode p = stack.pop();return list.get(list.size()-k);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {int ret;int count;public int kthSmallest (TreeNode root, int k) {return ret;public void dfs (TreeNode root,int k) {if (root.left!=null )dfs(root.left,k);if (++count==k){return ;if (root.right!=null )dfs(root.right,k);
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数 distance 。
如果二叉树中两个 叶 节点之间的 最短路径长度 小于或者等于 distance ,那它们就可以构成一组 好叶子节点对 。
返回树中 好叶子节点对的数量 。
示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入: root = [1,2,3,null,4], distance = 3\ \
解题思路
父节点和子节点的距离是 1
对树后序遍历 ,需要返回这个节点到其下方所有叶子节点的距离
这样就可以将这个节点的左子树所有叶子节点和右子树所有叶子节点都凑个对
然后将所有叶子节点不超过距离的弄到一起返回
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution {private int ans = 0 ;public int countPairs (TreeNode root, int distance) {return ans;private List<Integer> dfs (TreeNode root, int distance) {if (root == null )return new ArrayList ();if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {new ArrayList ();0 );return list;new ArrayList ();for (int it : left) {if (++it > distance)continue ;for (int it : right) {if (++it > distance)continue ;for (int l : left) {for (int r : right) {if (l + r + 2 <= distance)return list;
题目描述
给定一个根为 root 的二叉树,每个节点的深度是 该节点到根的最短距离 。 如果一个节点在 整个树 的任意节点之间具有最大的深度,则该节点是 最深的 。 一个节点的 子树 是该节点加上它的所有后代的集合。 返回能满足 以该节点为根的子树中包含所有最深的节点 这一条件的具有最大深度的节点。
说的云里雾里,人话:最深叶子节点的最近公共祖先
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
解题思路
对于一个节点,如果左子树高度==右子树高度,这个节点就是答案,如果左子树高度<右子树高度,查找右子树,否则查找左子树
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return null ;else {int ldep = maxDepth(root.left), rdep = maxDepth(root.right);if (ldep == rdep) return root;else if (ldep > rdep) return subtreeWithAllDeepest(root.left);else return subtreeWithAllDeepest(root.right);int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;else return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1 ;
题目描述
给定一棵二叉树,其中每个节点都含有一个整数数值(该值或正或负)。设计一个算法,打印节点数值总和等于某个给定值的所有路径的数量。注意,路径不一定非得从二叉树的根节点或叶节点开始或结束,但是其方向必须向下(只能从父节点指向子节点方向)。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 5
返回:3 解释:和为 22 的路径有:[5,4,11,2], [5,8,4,5], [4,11,7]
解题思路
求出当前节点为根路径是否满足,递归判断每个节点
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {int count = 0 ;public int pathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;if (root.left != null ) pathSum(root.left, sum);if (root.right != null ) pathSum(root.right, sum);return count;public void helper (TreeNode node, int sum) {if (sum == node.val) count++;if (node.left != null ) helper(node.left, sum - node.val);if (node.right != null ) helper(node.right, sum - node.val);
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
解题思路
广度优先遍历,采用队列获取其每层的长度
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();if (!Objects.isNull(root)) queue.add(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null ) queue.add(node.left);if (node.right != null ) queue.add(node.right);return result;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root==null )return ret;new LinkedList <>();while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();new ArrayList <>();for (int i=0 ;i<size;i++){TreeNode p = queue.pop();if (p.left!=null )queue.offer(p.left);if (p.right!=null )queue.offer(p.right);return ret;
解题思路
对树DFS判断其目标节点是否存在,如果存在返回true寻找另一个节点,当两个节点都找到,递归返回获得其第一个公共节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || p == root || q == root)return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);if (left!=null && right != null )return root;return left == null ? right : left;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {TreeNode ancestor = root;while (true ) {if (p.val < ancestor.val && q.val < ancestor.val) {else if (p.val > ancestor.val && q.val > ancestor.val) {else {break ;return ancestor;public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor0 (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root==q||root==p||root==null )return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);if (left!=null &&right!=null )return root;return left!=null ?left:right;
题目描述
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
示例 :
返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
注意:两结点之间的路径长度是以它们之间边的数目表示。
解题思路
深度优先搜索,分别递归计算每个节点的左右子树的路径之和,默认值为1超过则更新,递归向上执行
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {int ans;public int diameterOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) {1 ;return ans - 1 ;public int depth (TreeNode node) {if (node == null ) return 0 ; int L = depth(node.left); int R = depth(node.right); 1 ); return Math.max(L, R) + 1 ;
题目描述
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层次遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
例如: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
返回锯齿形层次遍历如下:
[
解题思路
广度优先遍历,每次将当前层元素出队,使用一个全局变量判断方向,调用addLast或者addFirst。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution {public void DFS (TreeNode node, int level, List<List<Integer>> results) {if (level >= results.size()) {new LinkedList <Integer>();else {if (level % 2 == 0 )else 0 , node.val);if (node.left != null ) DFS(node.left, level + 1 , results);if (node.right != null ) DFS(node.right, level + 1 , results);public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return new ArrayList <List<Integer>>();new ArrayList <List<Integer>>();0 , results);return results;public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();if (root==null )return ant;new LinkedList <>();boolean flag = false ;while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();new LinkedList <>();for (int i=0 ;i<size;i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left!=null )queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right!=null )queue.offer(node.right);if (flag)return ant;
解题思路
递归每次递归返回+1,返回左右节点较大的值。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {if (Objects.isNull(root)) return 0 ;return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int minDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;if (root.left == null && root.right != null ) {return 1 + minDepth(root.right);if (root.right == null && root.left != null ) {return 1 + minDepth(root.left);return 1 + Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right));
题目描述
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 输入:
解释: 输入为: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]。 根节点的值为 5 ,但是其右子节点值为 4 。
解题思路
获取左右子书的边界值,递归判断每一个节点是否满足条件
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {return dfs(root,Long.MAX_VALUE,Long.MIN_VALUE);public boolean dfs (TreeNode root,long max,long min) {if (root==null )return true ;if (root.val>=max||root.val<=min)return false ;return dfs(root.left,root.val,min) && dfs(root.right,max,root.val);
题目描述
给定一个非空二叉树,返回其最大路径和。
思路
后序递归遍历,判断其左右子树最大值,依此递归
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public int maxPathSum (TreeNode root) {return ans;public int max (TreeNode root) {if (Objects.isNull(root)) return 0 ;int left = Math.max(max(root.left), 0 );int right = Math.max(max(root.right), 0 );return Math.max(left, right) + root.val;
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) {new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++)map.put(inorder[i], i);return buildTree(preorder,0 ,preorder.length-1 ,inorder,0 ,inorder.length-1 ,map);buildTree (int [] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,int [] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, Map<Integer, Integer> inMap) {if (preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) return null ;TreeNode root = new TreeNode (preorder[preStart]);int inRoot = inMap.get(root.val);int numsLeft = inRoot - inStart;1 , preStart + numsLeft,inorder, inStart, inRoot - 1 , inMap);1 , preEnd,inorder, inRoot + 1 , inEnd, inMap);return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {/ / 思路:递归/ / 遍历指的是根节点遍历的顺序/ / 后序中最后一个节点为根节点,中序根节点左边全部为根节点左子树,递归缩小范围int [] inorder, int [] postorder) {< Integer ,Integer > map = new HashMap<> ();for (int i= 0 ;i< inorder.length;i+ + )map.put(inorder[i],i);return buildTree(inorder,0 ,inorder.length-1 ,postorder,0 ,postorder.length-1 ,map);int [] inorder,int inStart,int inEnd, int [] postorder,int postStart,int postEnd,Map< Integer ,Integer > map){> inEnd|| postStart> postEnd)return null ;= new TreeNode(postorder[postEnd]);int index = map.get(node.val);/ / 获取当前根节点所在中序数组的位置int num = index - inStart;/ / 当前左子树的节点数量/ / 递归构建左子树: / / 此时中序范围为inStart到当前节点在中序数组中的位置减一,即[inStart,index-1 ]/ / 因为后续遍历最后一个值为根节点,此时后续范围开始下标为postStart,结束下标为当前后续开始下标+ 左子树还有的节点数量-1 ,即[postStart,postStart+ num-1 ]= buildTree(inorder,inStart,index-1 ,postorder,postStart,postStart+ num-1 ,map);/ / 递归构建右子树:/ / 此时中序范围为当前节点在中序数组中的位置加一到inEnd,即[index+ 1 ,inEnd]/ / 此时后续遍历的开始为上面左子树的结束+ 1 ,即 postStart+ num ,结束为postEnd-1 ,减一是因为当前节点已经作为根节点使用= buildTree(inorder,index+ 1 ,inEnd,postorder,postStart+ num,postEnd-1 ,map);return node;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public TreeNode constructFromPrePost (int [] preorder, int [] postorder) {int m = preorder.length;int n = postorder.length;new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) postMap.put(postorder[i],i);return buildTree(preorder,0 ,m-1 ,postorder,0 ,n-1 ,postMap);public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder,int preStart,int preEnd, int [] postorder,int postStart,int postEnd,Map<Integer,Integer> postMap) {if (preStart>preEnd||postStart>postEnd)return null ;TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode (preorder[preStart]);if (preStart==preEnd)return newNode;int index = postMap.get(preorder[preStart+1 ]);int num = index-postStart;1 ,preStart+num+1 ,postorder,postStart,index,postMap);2 ,preEnd,postorder,index+1 ,postEnd-1 ,postMap);return newNode;
解题思路
回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public List<TreeNode> generateTrees (int n) {if (n == 0 ) {return new LinkedList <TreeNode>();return generateTrees(1 , n);public List<TreeNode> generateTrees (int start, int end) {new LinkedList <TreeNode>();if (start > end) {null );return allTrees;for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {1 );1 , end);for (TreeNode left : leftTrees) {for (TreeNode right : rightTrees) {TreeNode currTree = new TreeNode (i);return allTrees;
二叉树的右视图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public List<Integer> rightSideView (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();if (root!=null )queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();for (int i=0 ;i<size;i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (i==size-1 )ans.add(node.val);if (node.left!=null )queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right!=null )queue.offer(node.right);return ans;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public int sumNumbers (TreeNode root) {return dfs(root, 0 );public int dfs (TreeNode root, int prevSum) {if (root == null ) {return 0 ;int sum = prevSum * 10 + root.val;if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) {return sum;else {return dfs(root.left, sum) + dfs(root.right, sum);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {return dfs(root,targetSum);public boolean dfs (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root==null )return false ;if (root.left==null &&root.right==null &&targetSum-root.val==0 )return true ;return dfs(root.left,targetSum-root.val)||dfs(root.right,targetSum-root.val);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {new LinkedList <Integer>());return ans;public void dfs (TreeNode root, int targetSum,LinkedList<Integer> path) {if (root==null )return ;int val = targetSum-root.val;if (root.left==null &&root.right==null &&val==0 ){new ArrayList (path));if (root.left!=null ){if (root.right!=null ){
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public int pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {new HashMap <>();0L , 1 );return dfs(root, prefix, 0 , targetSum);public int dfs (TreeNode root, Map<Long, Integer> prefix, long curr, int targetSum) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int ret = 0 ;0 );0 ) + 1 );0 ) - 1 );return ret;int ret;public int pathSumDFS (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root==null )return ret;0 ,targetSum);return ret;public void dfs (TreeNode root,int v,int targetSum) {if (v==targetSum)ret++;if (root.left!=null )dfs(root.left,v,targetSum);if (root.right!=null )dfs(root.right,v,targetSum);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) {if (root==null ||(root.left==null &&root.right==null ))return root;TreeNode left = root.left;return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) {return dfs(root.left,root.right);public boolean dfs (TreeNode left,TreeNode right) {if (left==null &&right==null )return true ;if (left==null ||right==null )return false ;return left.val==right.val && dfs(left.right,right.left) && dfs(left.left,right.right);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {/ / 思路:中序遍历/ / 记录前置节点和头结点= = null ) return null ;/ / 空直接返回/ / = pre;/ / 处理头结点= head;return head;/ / dfs(cur): 递归法中序遍历;/ / 终止条件: 当节点 cur 为空,代表越过叶节点,直接返回;/ / 递归左子树,即 dfs(cur.left) / / 构建链表:/ / 当 pre 为空时: 代表正在访问链表头节点,记为 head / / 当 pre 不为空时: 修改双向节点引用,即 pre.right = cur , cur.left = pre / / 保存 cur : 更新 pre = cur ,即节点 cur 是后继节点的 pre / / 递归右子树,即 dfs(cur.right) = = null ) return ;/ / 先遍历左结点!= null ) pre.right = cur;/ / 如果有前驱节点则前驱节点right (下一个节点)执行当前节点else head = cur;/ / 记录头结点= pre;/ / 当前节点的left 指向pre= cur;/ / 更新前驱节点/ / 后遍历右边节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {/ / 完全二叉树bfs时null 总会在队尾,如果存在队列中间有null 则非完全二叉树boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {< TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<> ();= q.removeFirst()) != null ) {/ / 无需做判断是空,方便后面判断/ / 如果是完全二叉树此时queue尾部装都为null / / 非完全会出现[node1,node2,null ,node3]的情况! q.isEmpty()) {!= null ) {return false ;return true ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Trie {= new TrieNode[26 ];boolean isEnd = false ;= new TrieNode();insert (String word) {= root;for (int i= 0 ;i< word.length();i+ + ){int index = word.charAt(i)- 'a' ;= = null ){= new TrieNode();= cur.next[index];= true ;boolean search (String word) {= root;for (int i= 0 ;i< word.length();i+ + ){int index = word.charAt(i)- 'a' ;= = null )return false ;= cur.next[index];return cur.isEnd;boolean startsWith(String prefix) {= root;for (int i= 0 ;i< prefix.length();i+ + ){int index = prefix.charAt(i)- 'a' ;= = null )return false ;= cur.next[index];return true ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution {/ / 思路:BFS/ / 完全二叉树的性质):对于一颗完全二插树,如果按照从上至下,从左往右对所有节点从零开始顺序编号/ / 则父节点的左孩子节点的序号:2 * i+ 1 父节点的左孩子节点的序号:2 * i+ 2 ;/ / 所以每层的宽度就可以使用:每层最后一个节点的值减去最后一个节点的值+ 1 / / 1 / / / \/ / 2 3 / / / \ / \/ / 4 5 6 7 int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {int ret = 0 ;< TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<> ();= 0 ;/ / 关键! queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();/ / 当前这层的宽度int width = queue.getLast().val- queue.getFirst().val+ 1 ;for (int i= 0 ;i< size;i+ + ){= queue.pop();!= null ){= 2 * node.val+ 1 ;/ / 左子树编号!= null ){= 2 * node.val+ 2 ;/ / 右子树编号/ / 更新宽度= Math.max (ret,width);return ret;/ / DFS< Integer , Integer > levelMin = new HashMap< Integer , Integer > ();int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {return dfs(root, 1 , 1 );int dfs(TreeNode node, int depth, int index) {= = null )return 0 ;/ / 每一层最先访问到的节点会是最左边的节点,即每一层编号的最小值return Math.max (index - levelMin.get(depth) + 1 , max (dfs(node.left, depth + 1 , index * 2 ), + 1 , index * 2 + 1 )));
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class Codec {/ / DFS遍历成字符串,当节点left 和right 为空记录为NULL = new StringBuilder();return reserialize(root);= = null )sb.append("NULL,");else {return sb.toString();/ / 递归解析树= data.split(",");< String> list = new LinkedList<> (Arrays.asList(nodes));return deserialize(list);< String> list) {equals (list.get(0 ))){0 );return null ;= new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(list.get(0 )));0 );= deserialize(list);= deserialize(list);return node;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public class Codec {public void postorder (TreeNode root, StringBuilder sb) {if (root == null ) return ;public String intToString (int x) {char [] bytes = new char [4 ];for (int i = 3 ; i > -1 ; --i) {3 - i] = (char ) (x >> (i * 8 ) & 0xff );return new String (bytes);public String serialize (TreeNode root) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();return sb.toString();public TreeNode helper (Integer lower, Integer upper, ArrayDeque<Integer> nums) {if (nums.isEmpty()) return null ;int val = nums.getLast();if (val < lower || val > upper) return null ;TreeNode root = new TreeNode (val);return root;public int stringToInt (String bytesStr) {int result = 0 ;for (char b : bytesStr.toCharArray()) {8 ) + (int )b;return result;public TreeNode deserialize (String data) {new ArrayDeque <Integer>();int n = data.length();for (int i = 0 ; i < (int )(n / 4 ); ++i) {4 * i, 4 * i + 4 )));return helper(Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, nums);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {/ / 思路:dfs递归交换左右节点return root;= = null )return root;left = dfs(root.left);right = dfs(root.right);= right ;= left ;return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return ret;new LinkedList <Integer>());return ret;public void backtrack (TreeNode root,LinkedList<Integer> path) {if (root==null )return ;if (root.left==null &&root.right==null ){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();for (int i=0 ;i<path.size();i++){if (i!=path.size()-1 )sb.append("->" );if (root.left!=null ){if (root.right!=null ){
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {boolean ret = false ;= = null )return false ;= = subRoot.val)ret = compare(root,subRoot);return ret || isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)|| isSubtree(root.right,subRoot);boolean compare(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){= = null || q= = null )return p= = q;!= q.val)return false ;return compare(p.left,q.left)&& compare(p.right,q.right);boolean isMatch;boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {= = subRoot.val){return true ;!= null )isSubtree(root.left,subRoot);!= null )isSubtree(root.right,subRoot);return isMatch;boolean dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot){= = null && subRoot= = null )return true ;= = null && subRoot!= null )|| (root!= null && subRoot= = null )|| root.val!= subRoot.val)return false ;return dfs(root.left,subRoot.left) && dfs(root.right,subRoot.right);
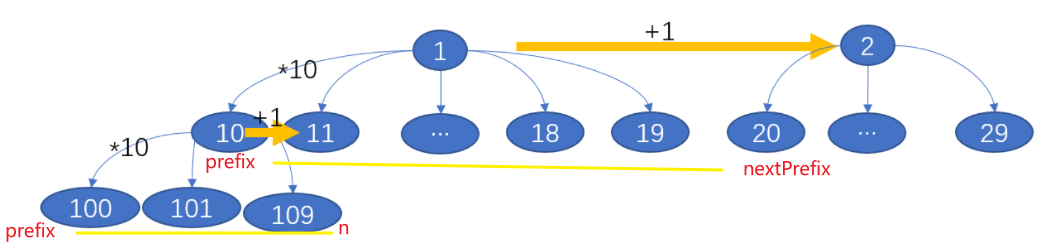
给定整数 n 和 k,返回 [1, n] 中字典序第 k 小的数字。
不难发现其实字典序就是对这棵十叉树进行**先序遍历 **得出,1,10,100,101….,110,111,……,先序遍历到k-n节点即是目标值。
实际上我们求出第k小的数需要解决的问题如下:
1.怎么确定一个前缀下所有子节点的个数?
2.如果第 k 个数在当前的前缀下,怎么继续往下面的子节点找?
3.如果第 k 个数不在当前的前缀,即当前的前缀比较小,如何扩大前缀,增大寻找的范围?
其实就是需要确定往数的下走还是右走,从而确定目标值的位置
1.怎么确定一个前缀下所有子节点的个数?通过上图我们可以发现
1为前缀所有节点计算方式=(第1层nextPrefix-prifix)+(第2层nextPrefix-prifix)+…+(第n层nextPrefix-prifix)
那么问题又来了我怎么确定他是第几层呢?其实题目给我们的n就是说一共有n个字段序的数,那我们查找的前缀节点的值自然只能小于等于n,所以当我们的prifix大于n时我们就需要跳出层级节点计算了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 / / 计算prefix下的节点个数int getCount(int prefix,int n){/ / 记录当前前缀= prefix;/ / 注意需要使用long来接收= prefix + 1 ;/ / 下一个节点的前缀/ / 记录峰头之间的累加int count = 0 ;<= n){/ / 累加每层之间的差值/ / 特别的 如果next已经大于n了的时候,因为要包含n 所以取n+ 1 个数+ = Math.min (next,n+ 1 )- curr;/ / 进入下一层* = 10 ;* = 10 ;return count;
2.如果第 k 个数在当前的前缀下,怎么继续往下面的子节点找?
1 2 3 int count = getCount(prefix,n);/ / 当前前缀下节点数* = 10 ;/ / 下沉一层+ + ;/ / 记录走过根节点
3.如果第 k 个数不在当前的前缀,即当前的前缀比较小,如何扩大前缀,增大寻找的范围?
1 2 3 int count = getCount(prefix,n);/ / 当前前缀下节点数+ + ;/ / 前缀右移,1 ,2 ,3. ..+ = getCount/ / 走过当前前缀下所有节点
完整的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution {/ / 思路:构建为十叉树int findKthNumber(int n, int k) {/ / 初始化的时候包含1 节点的,所以数量是1 int res = 1 ;/ / 默认是从1 节点开始遍历,所以是1 int prefix = 1 ;< k){/ / 计算当前分支下,如果跳到下一个峰,有多少节点数int count = getCount(prefix,n);/ / 如果加上跨越到下一个峰的数量大于了目标k,则不能跳跃+ count> k){/ / 走到下一层* = 10 ;/ / 因为走过了根节点,所以需要加一+ + ;else {/ / 如果不大于的话直接加上走下一个分支+ = count;+ + ;return prefix;/ / 计算int getCount(int prefix,int n){/ / 记录当前前缀= prefix;= prefix + 1 ;/ / 下一个节点的前缀/ / 记录峰头之间的累加int count = 0 ;<= n){/ / 累加每层之间的差值/ / 特别的 如果next已经大于n了的时候,因为要包含n 所以取n+ 1 个数+ = Math.min (next,n+ 1 )- curr;/ / 进入下一层* = 10 ;* = 10 ;return count;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {/ / 节点在的位置可能性/ / 1. 根节点()/ / 2. 叶子节点(直接删掉)/ / 3. 待删除的节点无左子树,有右子树/ / 4. 待删除的节点有左子树,无右子树/ / 5. 待删除的节点有左子树、右子树(左子树作为新的代替节点,右子树插入左子树最右边的节点)int key) {/ / 1 = = null )return root;> key){= deleteNode(root.left,key);else if(root.val< key){= deleteNode(root.right,key);else if(root.val = = key){= = null && root.right= = null )return null ;/ / 2 = = null && root.right!= null )return root.right;/ / 3 != null && root.right= = null )return root.left;/ / 4 / / 5 != null && root.right!= null ){/ / 获取左子树的最右边节点left = root.left;!= null )left = left.right;= root.right;return root.left;return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {/ / 思路:递归先遍历左子树,设置其right ,再返回其左子树最大节点= = null )return ;/ / 特殊条件/ / 开始递归right = root.right;left = root.left;= = null && root.right= = null )return root;/ / 左子树最后一个节点直接返回= null ;/ / 返回回来的最大节点/ / 左子树还有节点优先进入递归!= null ){= root.left;/ / 可设置root.right为左子树= recursion(left );/ / 如果当前节点有左右子树,需要将左子树返回回来的节点作为最大节点设置right != null && right != null ){= right ;right );/ / 如果当前节点只要右子树,直接进入右子树递归right != null )ret = recursion(right );= null ;/ / 左子树置空return ret;/ / 返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution {/ / 递归遍历树boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {= = null || q= = null )return p= = q;!= q.val) return false ;return isSameTree(p.left,q.left)&& isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {private List<List<Integer>> ret;public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int target) {new ArrayList <>();if (root==null )return ret;new LinkedList <>(),target);return ret;public void backtrack (TreeNode root,LinkedList<Integer> path, int target) {if (target==0 &&root.left==null &&root.right==null ){new ArrayList (path));return ;if (root.left!=null ){if (root.right!=null ){
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) {return helper(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 );public TreeNode helper (int [] nums, int left, int right) {if (left > right) return null ;int mid = (left + right) / 2 ;TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[mid]);1 );1 , right);return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 class Solution {public void recoverTreeOn (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return ;new Stack <>();new ArrayList <>();while (root!=null ||!stack.isEmpty()){while (root!=null ){if (!stack.isEmpty()){null ;for (int i=0 ;i<list.size();i++){if (list.get(i).val>list.get(i+1 ).val){break ;null ;for (int i=list.size()-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){if (list.get(i).val<list.get(i-1 ).val){break ;int tmp = val1.val;public void recoverTree (TreeNode root) {TreeNode x = null , y = null , pred = null , predecessor = null ;while (root != null ) {if (root.left != null ) {while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != root) {if (predecessor.right == null ) {else {if (pred != null && root.val < pred.val) {if (x == null ) {null ;else {if (pred != null && root.val < pred.val) {if (x == null ) {public void swap (TreeNode x, TreeNode y) {int tmp = x.val;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public Node connect (Node root) {if (root == null ) return null ;if (root.left != null ) {if (root.next != null ) {return root;public Node connectbfs (Node root) {new LinkedList <>();if (root==null )return root;while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();Node prev = null ;for (int i=0 ;i<size;i++){Node node = queue.pop();if (prev!=null )prev.next = node;if (node.left!=null )queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right!=null )queue.offer(node.right);return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution {Node last = null , nextStart = null ;public Node connect (Node root) {if (root == null ) return null ;Node start = root;while (start != null ) {null ;null ;for (Node p = start; p != null ; p = p.next) {if (p.left != null ) handle(p.left);if (p.right != null ) handle(p.right);return root;public void handle (Node p) {if (last != null ) last.next = p;if (nextStart == null ) nextStart = p;public Node connect (Node root) {if (root==null )return root;new LinkedList <>();while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();Node prev = null ;for (int i=0 ;i<size;i++){Node node = queue.pop();if (prev!=null )prev.next = node;if (node.left!=null )queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right!=null )queue.offer(node.right);null ;return root;
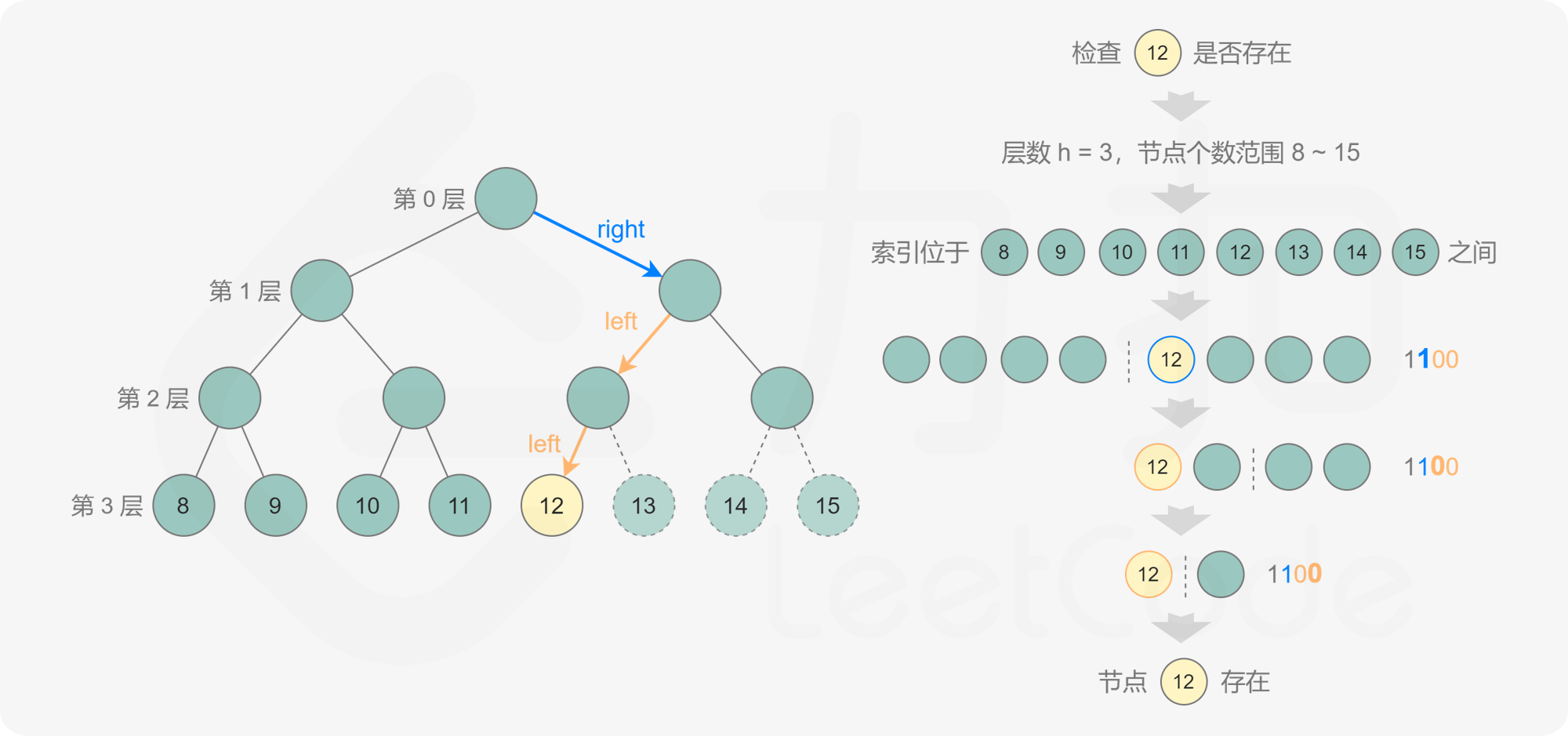
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class Solution {public int countNodes (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int level = 0 ;TreeNode node = root;while (node.left != null ) {int low = 1 << level, high = (1 << (level + 1 )) - 1 ;while (low < high) {int mid = (high - low + 1 ) / 2 + low;if (exists(root, level, mid)) {else {1 ;return low;public boolean exists (TreeNode root, int level, int k) {int bits = 1 << (level - 1 );TreeNode node = root;while (node != null && bits > 0 ) {if ((bits & k) == 0 ) {else {1 ;return node != null ;int ret;public int countNodesOn (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return 0 ;return countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right)+1 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();new HashMap <>();public List<Integer> distanceK (TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int k) {null ,0 ,k);return ret;public void setParent (TreeNode root) {if (root.left!=null ){if (root.right!=null ){public void findAns (TreeNode root,TreeNode from,int depth,int k) {if (root==null )return ;if (depth==k){ret.add(root.val);return ;}if (root.left!=from)findAns(root.left,root,depth+1 ,k);if (root.right!=from)findAns(root.right,root,depth+1 ,k);if (parent.get(root.val)!=from)findAns(parent.get(root.val),root,depth+1 ,k);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int numTrees (int n) {int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ];0 ] = 1 ;1 ] = 1 ;for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j <= i; j++) {1 ] * dp[i - j];return dp[n];
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {int ret;int maxDepth;public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) {1 );return ret;public void dfs (TreeNode root,int dpeth) {if (root==null )return ;if (dpeth>maxDepth){if (root.left!=null ){else if (root.right!=null ) {if (root.left!=null )dfs(root.left,dpeth+1 );if (root.right!=null )dfs(root.right,dpeth+1 );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) {while (root!=null ){if (root.val==val)return root;return null ;public TreeNode searchBST0 (TreeNode root, int val) {if (root==null )return null ;if (root.val==val)return root;return root.val>val ? searchBST(root.left,val): searchBST(root.right,val);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {int ret;public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return 0 ;if (root.left!=null &&root.left.left==null &&root.left.right==null )ret+=root.left.val;if (root.left!=null )sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);if (root.right!=null )sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);return ret;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {if (t1 == null ) return t2;if (t2 == null ) return t1;TreeNode merged = new TreeNode (t1.val + t2.val);return merged;public TreeNode mergeTrees0 (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {if (root1==null &&root2==null )return null ;if (root1==null )root1 = new TreeNode ();null ?0 :root2.val;if (root1.left==null &&root2!=null &&root2.left!=null )root1.left = new TreeNode ();if (root1.right==null &&root2!=null &&root2.right!=null )root1.right = new TreeNode ();if (root2!=null )mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);if (root2!=null )mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);return root1;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {int pre;int ans;public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) {1 ;return ans;public void dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return ;if (pre == -1 ) {else {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class BSTIterator {private int index;private List<Integer> data;public BSTIterator (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();int index = 0 ;new Stack <>();while (root!=null ||!stack.isEmpty()){while (root!=null ){if (!stack.isEmpty()){public int next () {return data.get(index++);public boolean hasNext () {return index<data.size();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public TreeNode insertIntoBST (TreeNode root, int val) {if (root==null )root=new TreeNode (val);if (val>root.val){if (root.right==null )root.right = new TreeNode (val);else insertIntoBST(root.right,val);if (val<root.val){if (root.left==null )root.left = new TreeNode (val);else insertIntoBST(root.left,val);return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public boolean isSubStructure (TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {if (A==null ||B==null )return false ;if (A.val==B.val && compare(A,B))return true ;return isSubStructure(A.left,B)|| isSubStructure(A.right,B);public boolean compare (TreeNode t1,TreeNode t2) {if (t1==null &&t2==null )return true ;if (t1==null &&t2!=null )return false ;if (t1!=null &&t2==null )return true ;if (t1.val!=t2.val)return false ;return compare(t1.left,t2.left) && compare(t1.right,t2.right);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Solution {public TreeLinkNode GetNext (TreeLinkNode pNode) {if (pNode==null )return null ;if (pNode.right==null ){if (pNode.next==null )return null ;if (pNode.next.left==pNode)return pNode.next;while (pNode.next!=null &&pNode.next.left!=pNode)pNode=pNode.next;return pNode.next;return dfs(pNode.right);public TreeLinkNode dfs (TreeLinkNode pNode) {if (pNode.left!=null )return dfs(pNode.left);return pNode;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {long sum;long best;public int maxProduct (TreeNode root) {long l = best * (sum - best);return (int )(l % 1000000007 );private long dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return 0 ;long cur = dfs(root.left)+dfs(root.right)+root.val;if (Math.abs(cur*2 -sum)<Math.abs(best*2 -sum))best=cur;return cur;public void sum (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {int layer;int ret;public int deepestLeavesSum (TreeNode root) {0 ,0 );return ret;public void dfs (TreeNode root,int lay,int sum) { if (lay==layer)ret+=root.val; if (lay>layer){if (root==null )return ;if (root.left!=null )dfs(root.left,lay+1 ,sum+root.val);if (root.right!=null )dfs(root.right,lay+1 ,sum+root.val);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {new ArrayList <>();public List<Integer> preorder0 (Node root) {if (root==null )return ret;for (Node node:root.children)preorder(node);return ret;public List<Integer> preorder (Node root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root==null )return ret;new Stack <>();while (!stack.isEmpty()){Node node = stack.pop();for (int i = node.children.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i) {return ret;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 class NumArray {int [] tree;int n;public NumArray (int [] nums) {new int [2 *n];public void buildTree (int [] nums) {for (int i = n, j = 0 ; i < 2 * n; i++, j++)tree[i] = nums[j];for (int i = n - 1 ; i > 0 ; --i)tree[i] = tree[i * 2 ] + tree[i * 2 + 1 ];public void update (int index, int val) {while (index>0 ){int left = index;int right = index;if (index % 2 == 0 ) right = index+1 ;else left = index - 1 ;2 ] = tree[left] + tree[right];2 ;public int sumRange (int left, int right) {int ret = 0 ;while (left<=right){if (left % 2 == 1 ){if (right % 2 == 0 ){2 ;2 ;return ret;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution {public boolean flipEquiv (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {if (root1 == root2)return true ;if (root1 == null || root2 == null || root1.val != root2.val)return false ;return (flipEquiv(root1.left, root2.left) && flipEquiv(root1.right, root2.right) || flipEquiv(root1.left, root2.right) && flipEquiv(root1.right, root2.left));
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution {int sum;public TreeNode convertBST (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return root;if (root.right!=null )convertBST(root.right);if (root.left!=null )convertBST(root.left);return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public TreeNode pruneTree (TreeNode root) {return root!=null &&root.left==null &&root.right==null &&root.val==0 ?null :root;public boolean dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return true ;boolean left = true ,right = true ;if (root.left!=null )left = dfs(root.left);if (root.right!=null )right = dfs(root.right);if (left)root.left = null ;if (right)root.right = null ;return left && right && root.val==0 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution {public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int L, int R) {if (root == null ) return root;if (root.val > R) return trimBST(root.left, L, R);if (root.val < L) return trimBST(root.right, L, R);return root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public TreeNode removeLeafNodes (TreeNode root, int target) {if (root==null )return root;if (root.left!=null )removeLeafNodes(root.left,target);if (root.right!=null )removeLeafNodes(root.right,target);if (root.left!=null &&root.left.val==target&&root.left.left==null &&root.left.right==null )root.left=null ;if (root.right!=null &&root.right.val==target&&root.right.left==null &&root.right.right==null )root.right=null ;return root.left==null &&root.right==null &&root.val==target?null :root;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {int ret;public int maxAncestorDiff (TreeNode root) {0 ,100000 );return ret;public void dfs (TreeNode root,int max,int min) {if (root==null )return ;if (root.left!=null )dfs(root.left,max,min);if (root.right!=null )dfs(root.right,max,min);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {int ret = 0 ;public int longestUnivaluePath (TreeNode root) {if (root==null )return 0 ;if (root.left!=null )longestUnivaluePath(root.left);if (root.right!=null )longestUnivaluePath(root.right);return ret;public int dfs (TreeNode root,int target) {if (root==null ||root.val!=target)return 0 ;int l = dfs(root.left,target);int r = dfs(root.right,target);int c = Math.max(l,r)+1 ;1 ),ret);return c;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {private int ans = 0 ;public int distributeCoins (TreeNode root) {return ans;public int lrd (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;if (root.left != null ){if (root.right != null ){1 );return root.val - 1 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class RangeModule {
相关资料
 上的信息。
上的信息。