理论知识
在图中,若节点的边用箭头标明了边是有方向性的,则称这样的图为有向图,否则称为无向图。
在有向图中边的箭头指入的节点数量则为该节点的入度,从该节点指出的边则称为出度。
图中边所标记的数
图的遍历
和多叉树的遍历很相似
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Graph{int v;< Integer > adj[];int num){= num;= new LinkedList[v];for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i+ + ) adj[i] = new LinkedList<> ();int v,int w){add (w);/ / 借助队列:每轮将当前轮遍历,将自节点入队列int s){boolean [] visited = new boolean [v];< Integer > queue = new LinkedList<> ();= true ;! queue.isEmpty()){Integer poll = queue.poll();/ / 输出遍历的节点< Integer > edges = adj[poll];for (Integer edge : edges) {! visited[edge]){= true ;/ / 借助栈:一直压栈直到,弹栈后遇到没遍历过的再次压栈,如此反复int s){boolean [] visited = new boolean [v];< Integer > stack = new Stack<> ();= true ;! stack.isEmpty()){Integer poll = stack.pop();< Integer > edges = adj[poll];for (Integer edge : edges) {! visited[edge]){= true ;static void main(String[] args) {= new Graph(4 );0 , 1 );0 , 2 );1 , 2 );2 , 0 );2 , 3 );3 , 3 );2 );2 );
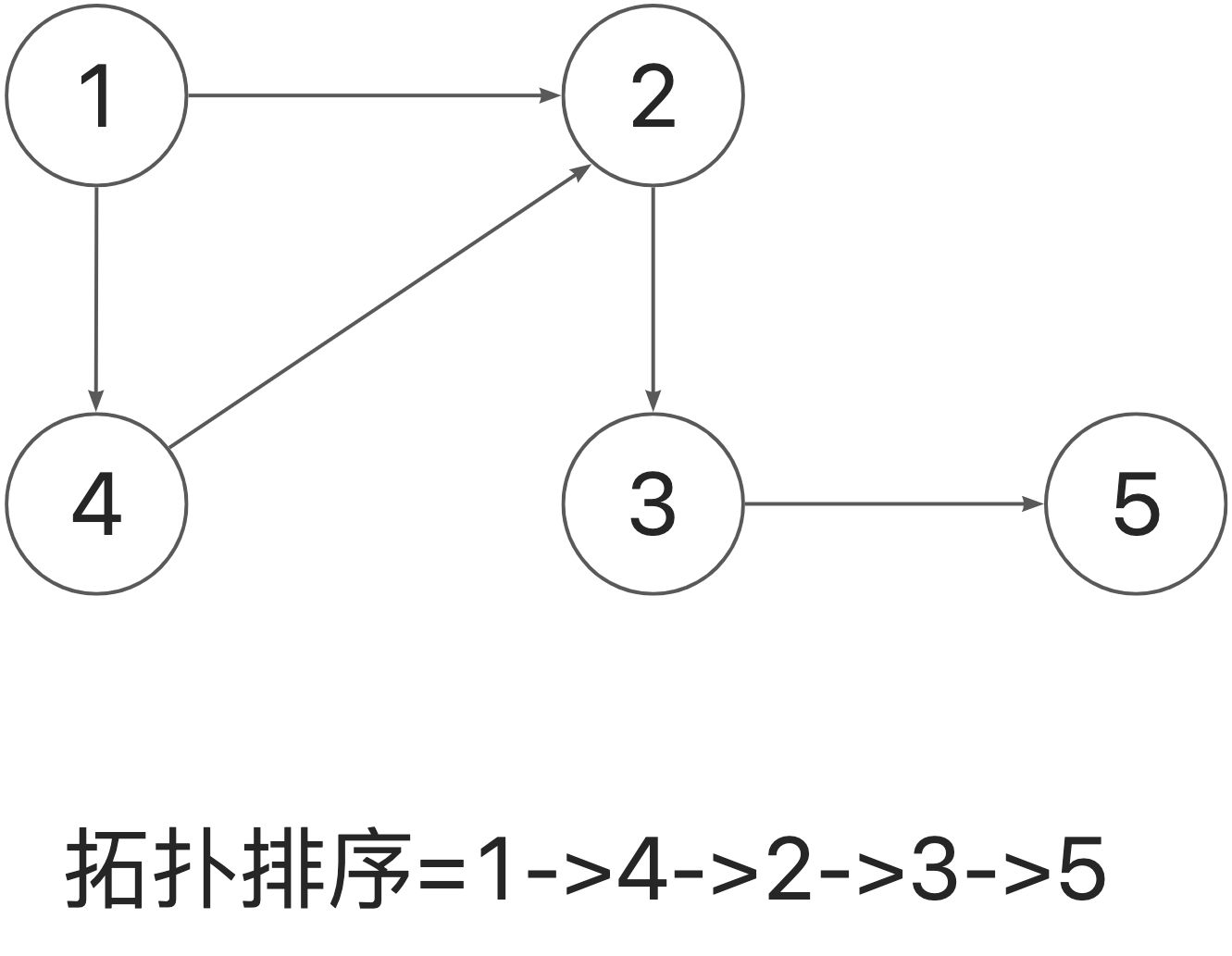
拓扑排序 对一个**有向无环图 (Directed Acyclic Graph简称DAG)G进行拓扑排序,是 将G中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点u和v,若边<u,v>∈E(G),则u在线性序列中出现在v之前 。通常,这样的线性序列称为满足拓扑次序(Topological Order)的序列,简称拓扑序列。简单的说, 由某个集合上的一个偏序得到该集合上的一个全序,这个操作称之为拓扑排序。**
实现拓扑的步骤
选择一个无前驱的节点开始(入度为0的节点)
从图中删除此顶点及所有出边。
重复上述两个步骤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 public class Graph {private int V;private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj;int v) {new ArrayList <>(v);for (int i = 0 ; i < v; ++i) adj.add(new ArrayList <>());void addEdge (int v, int w) {void topologicalSort (int v, boolean visited[], Stack<Integer> stack) {true ;while (it.hasNext()) {if (!visited[i]) topologicalSort(i, visited, stack);new Integer (v));void topologicalSort () {new Stack <>();boolean visited[] = new boolean [V];for (int i = 0 ; i < V; i++) {if (visited[i] == false ) {while (stack.empty() == false ) System.out.print(stack.pop() + " " );public static void main (String args[]) {Graph g = new Graph (6 );5 , 2 );5 , 0 );4 , 0 );4 , 1 );2 , 3 );3 , 1 );
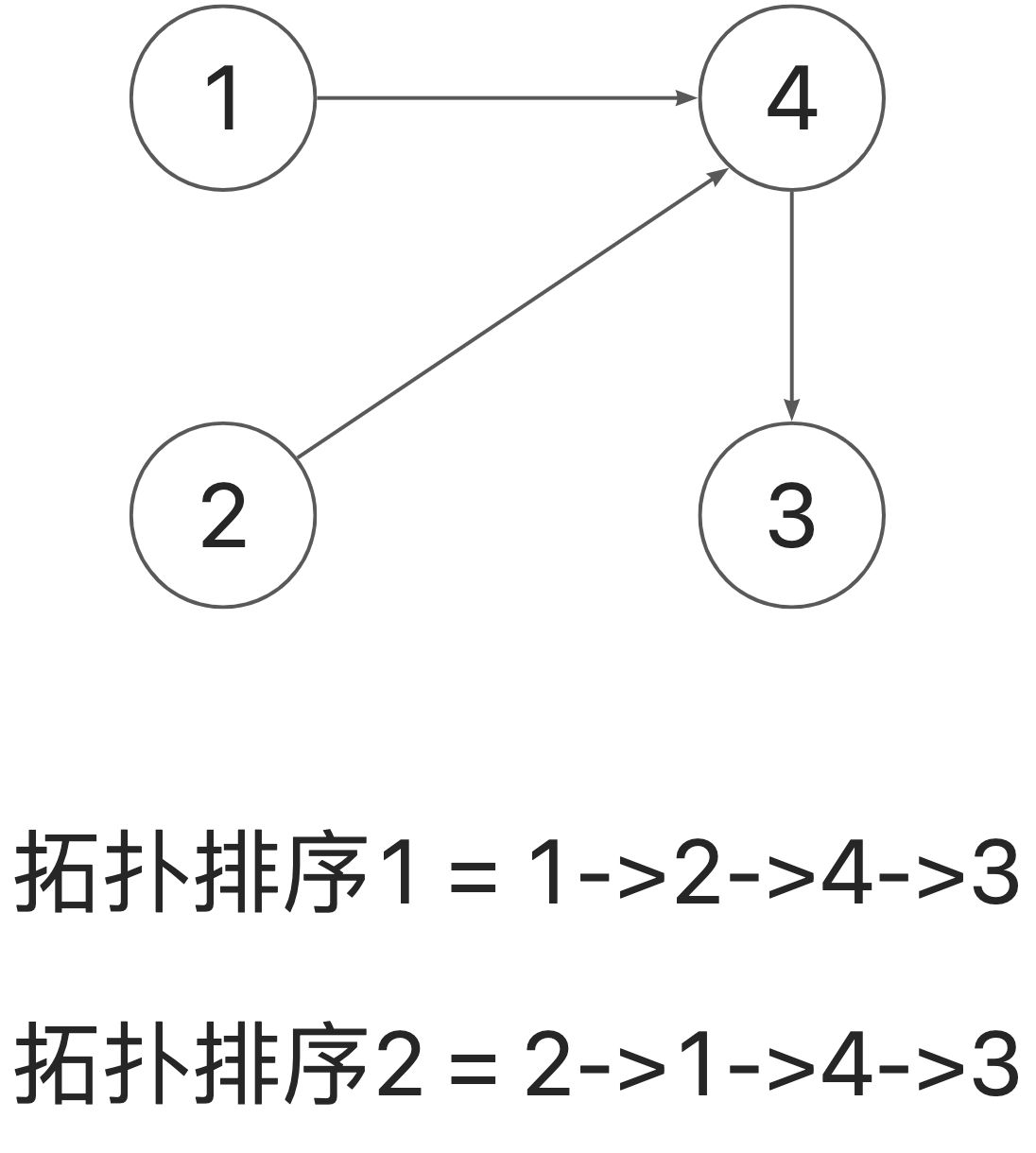
如何维护字典序最小的拓扑序?什么是最小子典序?
简单的理解方法是,把两种解看作两个数字1243 和 2143,小的那个数对应的排列就是字典序偏小的。
相关算法 Dijkstra 算法
最短路径算法
Prim 算法 Kruskal 算法 Bellman-Ford 算法 基于「队列」优化的 Bellman-Ford 算法 — SPFA 算法
拓扑排序之 Kahn 算法 相关题目 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution {int secondMinimum(int n, int [][] edges, int time , int change) {< Integer > [] graph = new List[n + 1 ];for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i+ + ) {= new ArrayList< Integer > ();for (int [] edge : edges) {0 ]].add (edge[1 ]);1 ]].add (edge[0 ]);/ / path[i][0 ] 表示从 1 到 i 的最短路长度,path[i][1 ] 表示从 1 到 i 的严格次短路长度int [][] path = new int [n + 1 ][2 ];for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i+ + ) {1 ][0 ] = 0 ;< int []> queue = new ArrayDeque< int []> ();new int []{1 , 0 });1 ] = = Integer.MAX_VALUE) {int [] arr = queue.poll();int cur = arr[0 ], len = arr[1 ];for (int next : graph[cur]) {+ 1 < path[next][0 ]) {0 ] = len + 1 ;new int []{next, len + 1 });else if (len + 1 > path[next][0 ] && len + 1 < path[next][1 ]) {1 ] = len + 1 ;new int []{next, len + 1 });int ret = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < path[n][1 ]; i+ + ) {% (2 * change) >= change) {= ret + (2 * change - ret % (2 * change));= ret + time ;return ret;
克隆图 (medium)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution {/ / bfs/ / 记录节点是否已经克隆:key= 旧节点,value = 新clone的节点< Node, Node> visited = new HashMap <> ();= = null ) return node;/ / 如果该节点已经被访问过了,则直接从哈希表中取出对应的克隆节点返回return visited.get(node);/ / 克隆节点,注意到为了深拷贝我们不会克隆它的邻居的列表= new Node(node.val, new ArrayList());/ / 哈希表存储/ / 遍历该节点的邻居并更新克隆节点的邻居列表for (Node neighbor: node.neighbors) {return cloneNode;/ / = = null ) return node;< Node, Node> visited = new HashMap();/ / 将题目给定的节点添加到队列< Node> queue = new LinkedList< Node> ();/ / 克隆第一个节点并存储到哈希表中new Node(node.val, new ArrayList()));/ / 广度优先搜索! queue.isEmpty()) {/ / 取出队列的头节点= queue.remove();/ / 遍历该节点的邻居for (Node neighbor: n.neighbors) {! visited.containsKey(neighbor)) {/ / 如果没有被访问过,就克隆并存储在哈希表中new Node(neighbor.val, new ArrayList()));/ / 将邻居节点加入队列中/ / 更新当前节点的邻居列表return visited.get(node);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {int [] visited;boolean valid = true ;public boolean canFinish (int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) {new ArrayList <>();new int [numCourses];for (int i=0 ;i<numCourses;i++)edges.add(new ArrayList <>());for (int [] pre:prerequisites)edges.get(pre[1 ]).add(pre[0 ]);for (int i=0 ;i<numCourses&&valid;i++)if (visited[i]==0 )dfs(i);return valid;public void dfs (int index) {1 ;for (int i:edges.get(index)){if (visited[i]==0 ){if (!valid)return ;else if (visited[i]==1 ){false ;return ;2 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution {int [] visited;int [] result;boolean valid = true ;int index;public int [] findOrder(int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) {new ArrayList <List<Integer>>();for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; ++i) {new ArrayList <Integer>());new int [numCourses];new int [numCourses];1 ;for (int [] info : prerequisites) {1 ]).add(info[0 ]);for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses && valid; ++i) {if (visited[i] == 0 ) {if (!valid) {return new int [0 ];return result;public void dfs (int u) {1 ;for (int v: edges.get(u)) {if (visited[v] == 0 ) {if (!valid) {return ;else if (visited[v] == 1 ) {false ;return ;2 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int scheduleCourse (int [][] courses) {1 ] - b[1 ]);new PriorityQueue <Integer>((a, b) -> b - a);int total = 0 ;for (int [] course : courses) {int ti = course[0 ], di = course[1 ];if (total + ti <= di) {else if (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek() > ti) {return q.size();
相关资料 https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/graph/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/breadth-first-search-or-bfs-for-a-graph/