背景
本文用于记录学习计算机局部性原理的相关笔记
详解
局部性原理是指CPU访问存储器时,无论是存取指令还是存取数据,所访问的存储单元都趋于聚集在一个较小的连续区域中。
时间局部性
时间局部性(Temporal Locality):如果一个信息项正在被访问,那么在近期它很可能还会被再次访问。
空间局部性
空间局部性(Spatial Locality):在最近的将来将用到的信息很可能与正在使用的信息在空间地址上是临近的。
顺序局部性
顺序局部性(Order Locality):在典型程序中,除转移类指令外,大部分指令是顺序进行的。顺序执行和非顺序执行的比例大致是5:1。此外,对大型数组访问也是顺序的。
应用
高速缓存,越接近cup的存储器速度越快容量越小,越远离cup的存储器速度越慢容量越大。
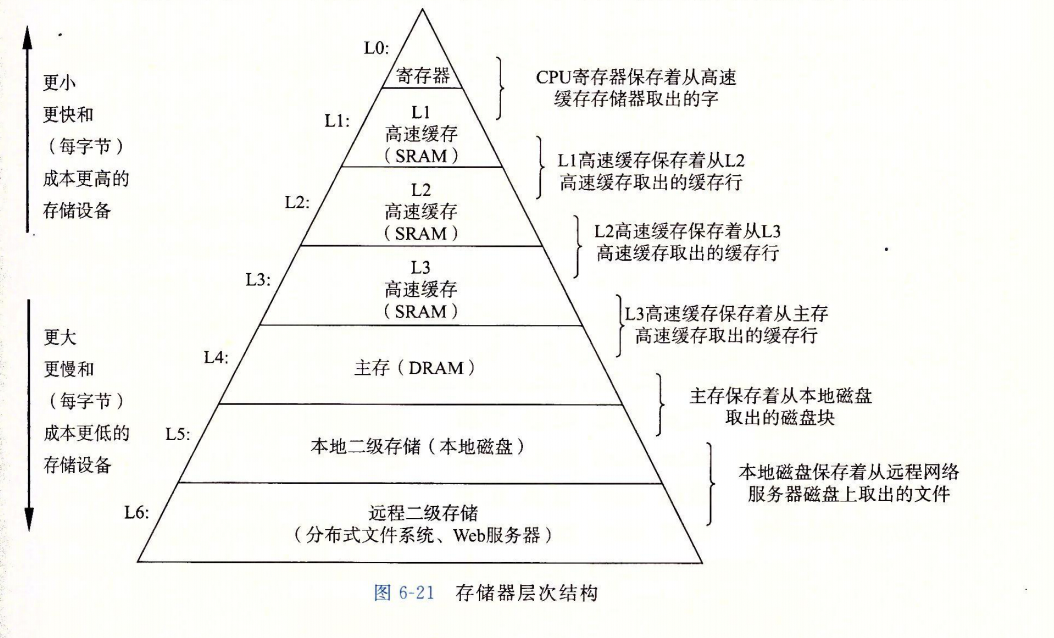
在查询数据过程中会优先在缓存中查找,L1->L2->L3…硬盘,我们知道缓存的大小有限,那么我们读取的数据会放入缓存中,如果我们频繁的读取那个数据,那可以直接在缓存中拿到,根据时间局部性和空间局部性原理设计的高速缓冲区能够极大提高数据的读取效率
案例
- 测试案例-数组访问
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[5000][5000];
for (int[] a:arr)Arrays.fill(a,1);
test1(arr);
test2(arr);
test3(arr);
}
public static void test1(int[][] arr) {
int ret = 0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5000; j++) {
ret+=arr[i][j];
}
}
long spend = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("耗时:"+spend+ " ms");
}
public static void test2(int[][] arr) {
int ret = 0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5000; j++) {
ret+=arr[j][i];
}
}
long spend = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("耗时:"+spend+ " ms");
}
public static void test3(int[][] arr) {
int ret = 0;
int[][] idx = new int[5000 * 5000][2];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 5000 * 5000; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt(5000);
int y = random.nextInt(5000);
idx[i] = new int[]{x,y};
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int[] site:idx) {
ret+=arr[site[0]][site[1]];
}
long spend = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("耗时:"+spend+ " ms");
}
|
总结
局部性原理,一个好的程序,在我们实际编码中如果想要提高程序的执行效率需要尽可能的使其满足局部性原理
资料
书籍:CSAPP Computer_Systems_A_Programmers_Perspective(3rd).pdf